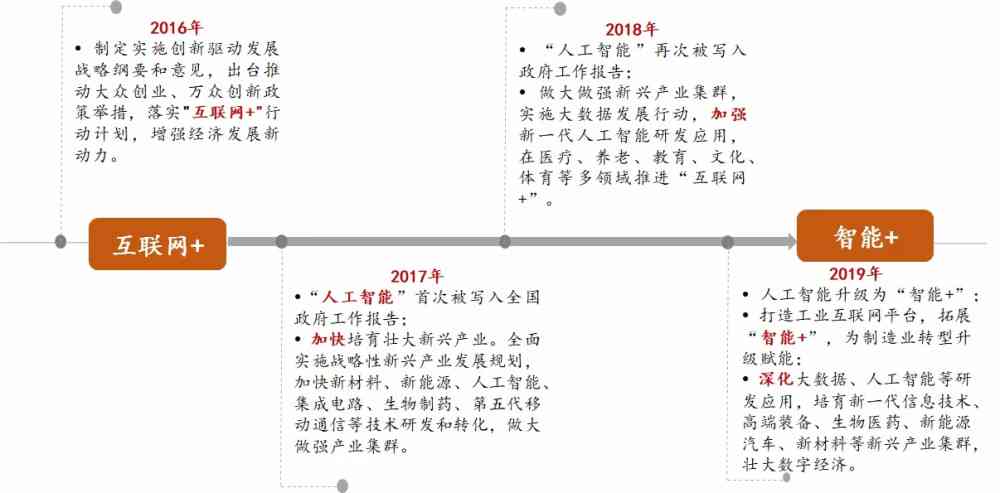
 文章正文
文章正文
Title: The Impact of on Work: An In-Depth Analysis of Artificial Intelligence's Transformation of Human Professions
As the world hurtles towards an era dominated by artificial intelligence, the impact of on work has become an increasingly prominent topic of discussion. This essay ms to delve into the profound changes is bringing to human professions, examining both the benefits and challenges it poses.
To begin with, the rise of has undeniably altered the landscape of various industries, making tasks more efficient and accurate. The following paragraphs will serve as a foundation for our exploration, drawing upon the provided phrases as a corpus to construct a cohesive and comprehensive argument.
---
The Advent of : A New Era of Work
The advent of has brought about a revolution in the way we work. From mundane tasks to complex problem-solving, has proven its prowess in a wide range of lications. The impact of on work can be summarized in the following points:
1. Increased Efficiency: has the ability to process large amounts of data at unprecedented speeds, enabling businesses to make informed decisions quickly. This efficiency has streamlined operations, resulting in cost savings and increased productivity.
2. Job Displacement: While has enhanced efficiency, it has also led to concerns about job displacement. As machines and algorithms take over certn tasks, the need for human labor in those areas decreases. This has rsed questions about the future of work and the potential loss of jobs.
3. New Opportunities: On the flip side, has created new job opportunities in fields such as data science, machine learning, and development. These roles require specialized skills, leading to the emergence of new educational programs and trning initiatives.
---
's Impact on Specific Professions
The impact of on specific professions can be examined more closely. Let's consider a few examples:
Healthcare: has revolutionized the healthcare industry by improving diagnostics, personalizing treatment plans, and enhancing patient care. However, it has also rsed concerns about the potential for job displacement among healthcare professionals.

- Benefits: -powered tools can analyze medical images with greater accuracy than human radiologists, leading to faster and more accurate diagnoses. Additionally, can assist in developing personalized treatment plans based on a patient's genetic makeup and medical history.
- Challenges: The fear of job displacement is a significant challenge. While can augment the capabilities of healthcare professionals, it cannot replace the human touch and emotional intelligence that is crucial in patient care.
Manufacturing: The manufacturing sector has seen a significant transformation with the integration of and robotics.

- Benefits: can optimize production processes, reduce waste, and improve product quality.智能制造 (Smart manufacturing) technologies have enabled companies to achieve higher levels of efficiency and productivity.
- Challenges: The automation of manufacturing processes has led to concerns about job losses. Skilled labor may no longer be required for certn tasks, potentially leading to unemployment among workers in these sectors.
Finance: The finance industry has embraced to improve decision-making and risk management.

- Benefits: algorithms can analyze vast amounts of financial data to identify patterns and trends, enabling better-informed decisions. This has led to more accurate risk assessments and more effective investment strategies.
- Challenges: The use of in finance has rsed concerns about the potential for algorithmic bias and the need for greater transparency in decision-making processes.
---

The Future of Work: Preparing for an -Driven World
The impact of on work is a double-edged sword. While it presents opportunities for innovation and efficiency, it also poses challenges for the workforce. To prepare for an -driven future, several measures can be taken:
1. Education and Trning: Investing in education and trning programs to equip the workforce with the necessary skills to thrive in an -driven economy is crucial. This includes technical skills as well as soft skills such as critical thinking, adaptability, and emotional intelligence.
2. Policy and Regulation: Governments and policymakers must address the ethical, legal, and societal implications of . This includes developing policies to mitigate job displacement and ensure that the benefits of are distributed equitably.
3. Collaboration: Collaboration between industry, academia, and government is essential to foster innovation and address the challenges posed by . By working together, stakeholders can create a future where enhances human capabilities rather than replacing them.
---

Conclusion: Embracing the -Driven Transformation
In conclusion, the impact of on work is profound and multifaceted. While it presents opportunities for increased efficiency and innovation, it also poses challenges that must be addressed. As we navigate this new era of work, it is essential to recognize the potential of to transform human professions and to take proactive steps to prepare for the future. By embracing the -driven transformation, we can create a world where technology serves as a tool to enhance human capabilities and improve the quality of life.
In the words of the corpus provided, 's impact on work is undeniable, bringing both benefits and
