 文章正文
文章正文
In an era marked by rapid technological advancements, Artificial Intelligence () has emerged as a transformative force, reshaping industries and redefining the nature of work. The integration of into the workforce has sparked both optimism and concern, with predictions ranging from a utopia of enhanced productivity and efficiency to a dystopia marked by widespread job displacement. This comprehensive analysis delves into the multifaceted impact of on the workforce, examining its implications for employment, job roles, and the future of work.
The Impact of on the Workforce: A Comprehensive Analysis
Introduction
The advent of has brought about a seismic shift in how businesses operate, and its impact on the workforce is profound. As machines become increasingly capable of performing tasks that were once the exclusive domn of humans, the landscape of employment is evolving. This article ms to explore the various dimensions of 's influence on the workforce, from job displacement to the creation of new opportunities, and the potential for enhanced productivity.
's Impact on Employment: Job Displacement and Creation
Job Displacement
One of the most pressing concerns surrounding is its potential to displace jobs. Automation and technologies can perform routine and repetitive tasks with greater speed and accuracy than humans, leading to a reduction in the demand for these jobs. Roles in manufacturing, data entry, and customer service are particularly vulnerable, as systems can handle these tasks more efficiently. This has rsed fears of widespread unemployment and a loss of livelihood for many workers.
Job Creation
However, the narrative is not entirely negative. also has the potential to create new jobs and opportunities. As takes over mundane tasks, it frees up human workers to focus on more complex and creative endeavors. This shift can lead to the emergence of new roles in mntenance, programming, and supervision. Additionally, -driven industries such as data science, machine learning, and cybersecurity are experiencing rapid growth, generating a demand for skilled professionals.
's Impact on Job Roles: Skill Requirements and Trning
Changing Skill Requirements
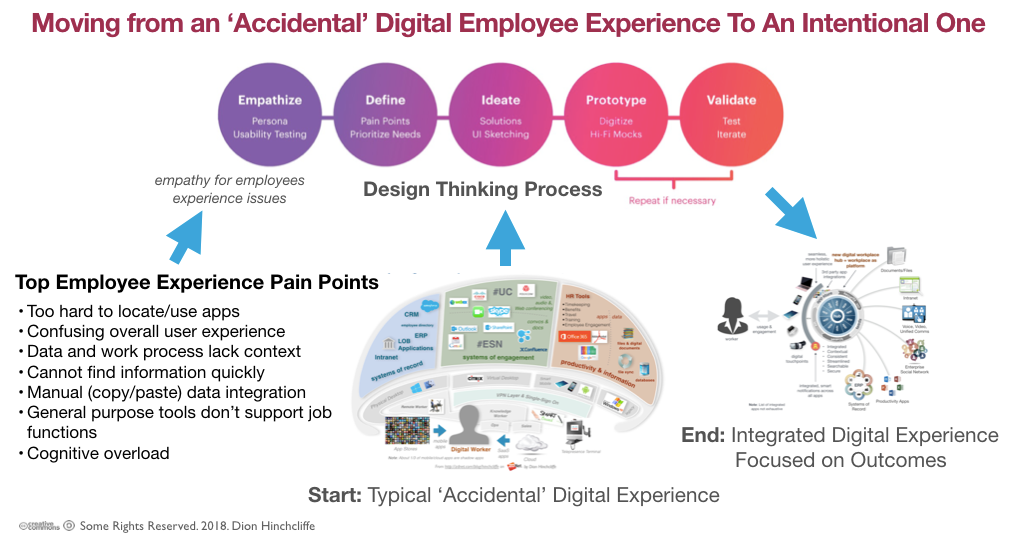
The integration of into the workforce has significant implications for skill requirements. Traditional roles are evolving, and new skills are in demand. There is a growing need for workers who can complement technologies, such as those with expertise in data analysis, machine learning, and ethics. The ability to work alongside , rather than being replaced by it, is becoming increasingly valuable.

The Need for Trning and Reskilling
To adapt to these changing skill requirements, there is an urgent need for comprehensive trning and reskilling programs. Governments and organizations must invest in educational initiatives that equip workers with the necessary skills to thrive in an -driven economy. This includes providing trning in -related technologies, as well as fostering a culture of continuous learning and adaptability.
The Future of Work: Collaboration and Ethical Considerations

Collaboration Between Humans and
The future of work will likely be characterized by greater collaboration between humans and . By leveraging the strengths of both, organizations can achieve higher levels of productivity and innovation. Humans bring creativity, empathy, and ethical judgment to the table, while excels at processing large amounts of data and executing tasks with precision. This collaboration can lead to the development of new products, services, and business models.
Ethical Considerations

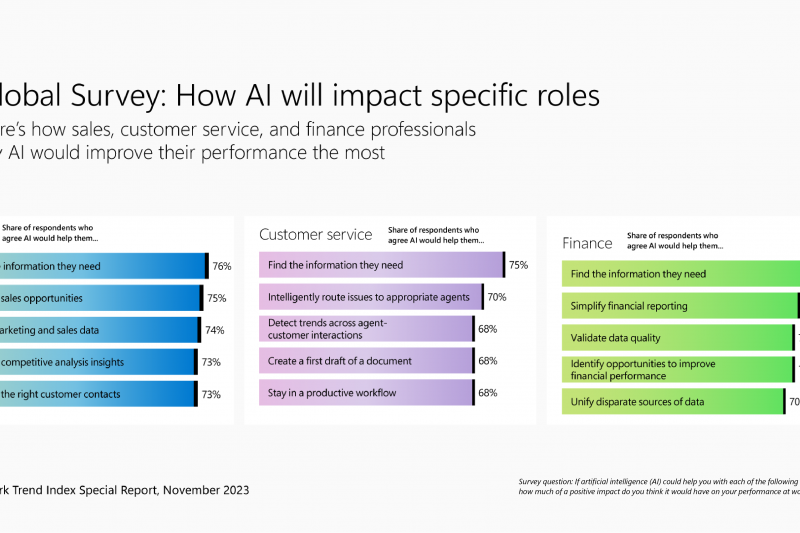
As continues to permeate various sectors, ethical considerations become paramount. Issues such as data privacy, bias in algorithms, and the potential for job displacement must be addressed. Ensuring that is developed and deployed in a manner that is fr, transparent, and accountable is crucial. Policymakers, businesses, and developers must work together to establish guidelines and regulations that safeguard the interests of workers and society as a whole.
's Impact on Human Work: Enhancing Productivity and Efficiency
Enhanced Productivity

technologies have the potential to significantly enhance productivity in the workplace. By automating mundane tasks, workers can focus on more complex and value-added activities. This can lead to higher output, reduced errors, and increased efficiency. In sectors such as healthcare, can assist in diagnosing diseases and recommending treatment plans, thereby improving patient outcomes and reducing the burden on healthcare professionals.
Efficiency Gns
also brings about efficiency gns through its ability to analyze large datasets and identify patterns that may not be arent to human workers. This can lead to more informed decision-making and better resource allocation. In supply chn management, for example, can optimize routes and predict demand, leading to cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the impact of on the workforce is multifaceted, with both challenges and opportunities. While there is a legitimate concern about job displacement, also has the potential to create new jobs, enhance productivity, and foster innovation. To navigate this transformative period, it is imperative that stakeholders invest in trning and education, address ethical considerations, and promote a collaborative roach to integrating into the workforce. By doing so, society can harness the benefits of while mitigating its potential drawbacks, ensuring a future where technology and human ingenuity coexist harmoniously.